Mechanobiology
Posted on
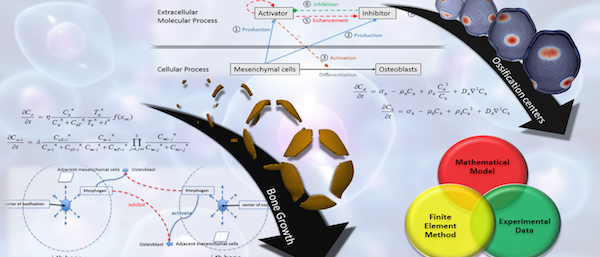
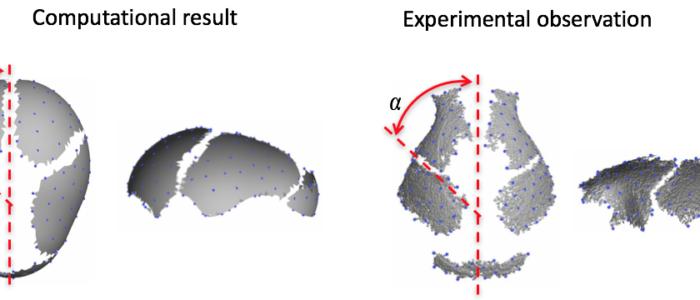
The PSU CBG research extends multiple length and time scales from whole body dynamics to cellular processes. Craniosynostosis is a common and complex craniofacial condition (~4 per 10,000 live births) that imposes a substantial financial and emotional burden on patients and their families. Craniosynostosis is a condition defined by premature closure of cranial vault sutures, which is associated with abnormalities of the brain and skull. Many causal relationships between discovered mutations and premature suture closure have been proposed but an understanding of the precise mechanisms remains elusive. This research develops a computational framework of biological processes underlying cranial growth that will enable a hypothesis driven investigation of craniosynostosis phenotypes using reaction-diffusion model and the finite element method. Primary centers of ossification in cranial vault are identified using an activator-inhibitor model that represents the behavior of key molecules for bone formation. Biomechanical effects due to the interaction between growing bone and soft tissue is investigated to elucidate the mechanism of growth of cranial vault.